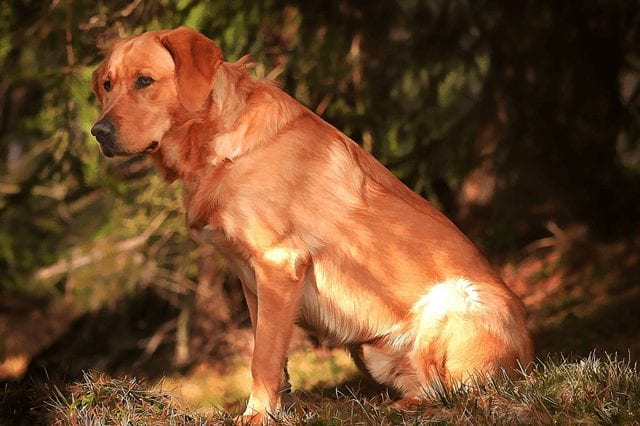
The red fox labrador is a color that does not render as much in the photo as it does in life: seen up close it looks so wonderful that it is difficult to take your eyes off it.
The red fox color does not represent a different color of the yellow labrador, but it is simply a darker shade: it is the ancient coloring of yellow, as it was at the beginning of its history when this type of coat was much more present, then it developed to lighter shades through the selection of breeders.
The Red Fox is nothing more than a darker variant in the shade of the yellow Labrador .
The American Kennel Club (US Registry of Purebred Dogs) clearly states that yellow Labradors can range in color from fox-red to lighter cream to white.
It follows that the term “red fox” to indicate the color of this Labrador is improper since it is always a yellow Labrador, although the comparison with other variants of yellow subjects may suggest that it is not.
Red Fox Labrador: History and Characteristics
From the very beginning of the Labrador’s history, most of the red fox subjects were selected from birth.
Through this selection of the darker color, in a fairly short time (in the first decades of their history), the fox red and dark yellow labrador retrievers were among the most popular.
In the past, however, fox red labradors were less common than black labradors: these dogs were used for work mainly in hunting: for this use, they tended to prefer black labradors over others.
The curious thing is that in the past fox red labradors were more common than light yellow ones: the first officially registered labrador in 1899 ( Ben of Hyde ) had a dark golden color, tending to fox red, a coat that was maintained at least until the 40s.
From the mid-1900s on, things changed: lighter yellow and cream-colored Labradors became more common than fox red ones by choice of breeders.

DNA, Chromosomes, Genes: The Ancestral Inheritance
In 1944, experiments conducted by Oswald Avery and colleagues identified DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) as the material in the cell responsible for carrying genetic information. Later, DNA was rightly called “the thread of life”.
The sequences of nucleotides, small molecules linked together that form two complementary chains to compose the native double helix shape of the DNA molecule, are responsible for coding specific proteins required for many cellular functions. These proteins are essential for the proper functioning of the organs which, in turn, are necessary for the normal function and duration of the whole organism.
In canine somatic cells (cells responsible for the composition of the body), DNA is packed into 78 chromosomes.
Thirty-nine of the chromosomes contain DNA transmitted, or inherited, from the father’s germ cell (sperm) and the other 39 contains DNA inherited from the mother’s germ cell (egg). Each chromosome, therefore, has a partner chromosome inherited from the other parent so that the 78 chromosomes form 39 pairs.
Germ cells differ from somatic cells in that they divide through a process known as meiosis. As a result of meiosis, each germ cell receives one of the partner chromosomes so that it has one chromosome of each type.
Meiosis, therefore, provides the means by which offspring can inherit genetic information from each parent while maintaining the same number of chromosomes in its somatic cells as found in the somatic cells of each parent and in other individuals within its species.
When germ cells fuse during fertilization they produce a single somatic cell from which offspring will develop. This somatic cell will divide to produce more cells through the mitosis process.
During mitosis, before a somatic cell divides, each chromosome will be duplicated so that a canine cell just before dividing will have 156 chromosomes (or 78 chromosome pairs).
When the somatic cell divides, each new cell will have the same amount of genetic information as the previous cell. Mitosis, therefore, provides the means for a single fertilized cell to develop into an entire organism, while maintaining the same number of chromosomes and the amount of genetic information in every cell in the body.
The composition of each of the chromosomes, the DNA to encode specific proteins that are responsible for producing individual genetic traits, or characteristics, are called genes.
Each gene encoding a specific protein is found in a particular site on the chromosome called the gene locus. The location of the gene locus for a trait on a chromosome will match the location of the gene locus for that same trait on its partner chromosome.
However, although the location of a gene locus is identical for each partner chromosome, the nucleotide sequence of the gene can be different on each of the two paired chromosomes.
When this happens and the DNA nucleotide sequence to encode a specific protein is altered, a condition referred to as a mutation, the resulting protein can physically and functionally differ from the normal protein.
For this reason, since more than one nucleotide sequence of a gene can be present at one gene locus on partner chromosomes, alternative sequences that control a particular trait are referred to as alleles.
The offspring can inherit the same allele at a particular gene locus from each parent. In that case, the offspring is considered homozygous for the particular trait governed by that gene locus. Alternatively, the offspring can inherit one allele from one parent but a different allele from the other parent. In this case, the progeny is considered heterozygous for that particular trait.
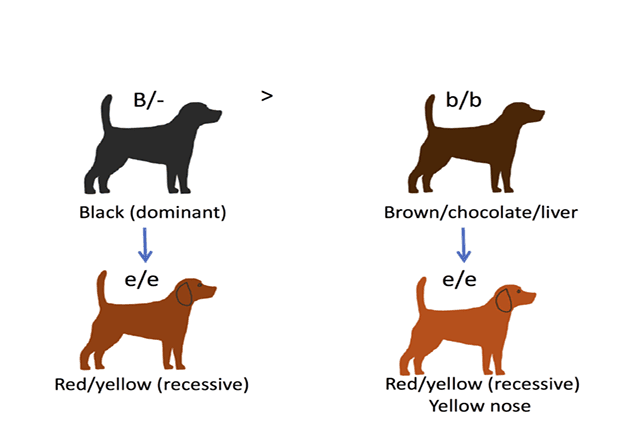
When offspring are heterozygous at a particular gene locus, often the characteristic of only one of the alleles will be expressed by the offspring. In this case, the allele that results in the expression of the trait is considered dominant with respect to the other allele that is considered recessive.
An example of dominant and recessive alleles, respectively, in the genetics of colors for the Labrador’s coat, is the ” B ” allele for the expression of black and the ” b ” allele for the expression of chocolate.
Black Labradors can be homozygous for black (BB) or heterozygous (Bb). In the latter case, the subject carries an allele for chocolate coloring, but his expression is masked by the dominant allele for black.
Heterozygous Labradors can only produce chocolate-colored offspring if they are born from a Labrador heterozygous or homozygous for the recessive “b” allele (chocolate Labrador). For a Labrador to appear chocolate, he must inherit the “b” allele from both parents.

Explanation Of The Red Fox Lab Color Genetics
As we know, the color of the coat is given by the presence of melanin (a substance that gives color and is produced by specific cells called melanosomes).
The color of melanosomes is linked to the amount of melanin that they themselves contain, in the hair, so there can be two types of this particular element: eumelanin which determines the presence of the black or brown color, and pheomelanin which instead determines the yellow color of the mantle.
The black coloration is due to specific genetic conditions and the necessary one is the presence of the B gene; here are the genotypes needed to obtain this particular pigmentation:
- BBEE genotype with the dominant B gene (black)
- BbEE genotype we will also have here a black Labrador but with the brown (b) recessive gene, therefore a black subject that transmits the color of the chocolate Labrador
- BbEe genotype (here you will have both the recessive brown and yellow gene but our Labrador will have a black pigmentation) – black that transmits yellow and brown
- genotype BBEe (also black with recessive yellow) – black that transmits yellow.
From the combinations of black, red, and white the different shades of colors. The study of coat color variations is the most complex and interesting subject that can fascinate a breeder, in order to be able to better select their bloodline.
The study of coat color variations began approximately in the early years of the last century, together with genetic evolution, after the rediscovery of Mendel’s laws.
In Labrador there are two groups of genes (E, B) that control the colors of the coat: one type (E or e) controls the colors black, chocolate (dark colors) and yellow (light colors).
Labradors with genotype EE (homozygous dominant) or genotype Ee (heterozygous) will be dark (black or chocolate), while Labradors with genotype ee (homozygous recessive) will be light (yellow or Dudley) ) because the genotype (e) represents the “NOT Yellow color).
The second group of genes affects dark color (B or b). These genes control that the black (dominant color) and brown (recessive) Labrador are dominant over the yellow color. The Labrador BB (dominant) or Bb will therefore be black.
The puppies will take an E / e (capital or lowercase) one from the mother and one from the father, as well as a B / b (capital or lowercase) to complete the genetic makeup.
B = Black
b = Brown
E = Color
e = No color (yellow)
A Labrador can have: BB, Bb, or bb along with EE, Ee, or ee
Since the two pairs of genes are paired, the possible combinations are:
- BBEE Black
- BBEe Black that transmits yellow
- BbEE Black that transmits brown
- BbEe Black that transmits yellow and brown
- BBee Yellow
- Bbee Yellow that transmits brown
- bbEE Brown
- bbEe Brown that transmits yellow
- bbee not allowed by the standard (yellow lab with light pigmentation – ‘Dudley’)
The genetic combination of eebb leads to a Labrador called “ Dudley “, which is a yellow Labrador with the pigmentation of chocolate Labrador.
This type of Labrador is not recognized by current official breed standards even though he is very likable!
A red labrador fox is simply a variation of yellow. The shade of yellow needed to produce the red coloration is controlled by a pigment called pheomelanin which is controlled by two other different sets of genes, A and C.
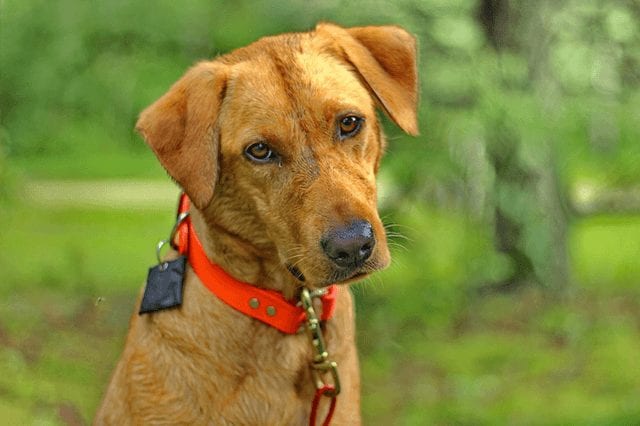

“ Red Fox Lab “ Puppies
As previously pointed out, red fox Labradors are present in fewer numbers today than in the past, while the lighter ones are much more common.
Why? The reasons could be the following:
- During the early years of the breed, dark yellow Labradors were more common, so yellow Labradors probably gave the idea of more exotic dogs, therefore rarer and more fascinating. For this reason, breeders would have started to select almost exclusively light yellow Labradors, decreasing fox red Labradors.
- Since the mid-1970s, Scottex has used a light yellow labrador as a mascot in its toilet paper advertisement. This commercial has been shot for years and years in more than 130 countries, and it is therefore very likely that the common idea of most people about the Labrador retriever is almost indissolubly linked to that of the light yellow Labrador.
Both of the events just mentioned probably played a major role in changing people’s perceptions of what a true yellow Labrador looks like.
It must also be said that although breeders have long selected mainly light yellow or cream-colored Labradors, in recent years the different shades of yellow Labradors have expanded again.
While in the past, pale yellow Labradors were seen as rarer, more exotic, and therefore more desirable, today it is the complete opposite, and “fox red” red fox Labradors are making a comeback.
Are red fox labradors purebred? Of course yes, precisely because their history dates back to the beginnings of the history of this breed.
Therefore it’s certain that they have never crossed with different breeds, unlike the Labrador Silver which is probably a genetic cross with the Weimaraner, in order to have their typical gray coat.
Traits of The Red Fox Lab
As noted above, color does not in any way affect the character of the animal.
Labradors have the following qualities :
- incredibly positive and friendly, they literally love everyone around;
- not predisposed to anger and aggression, suitable for young families with children;
- get along easily with other pets;
- strive to please the owner and be useful;
- active, lovers of frolic in the fresh air;
- trainable, even an unprepared owner can handle it.
Dogs of this breed are very attached to their owners. In their absence or with a lack of attention, the animal can bully and howl out of boredom.
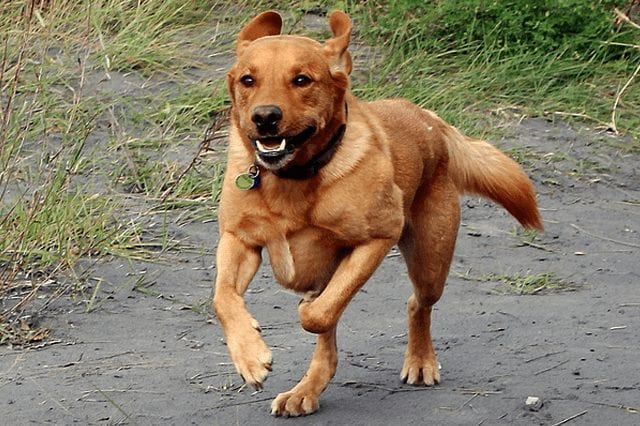

Pros and Cons
You can add to the above positive qualities :
- an innate hunting instinct. These Dogs have an excellent instinct, which helps them easily track prey or a shot bird.
- They are very smart and efficient. They work as bloodhounds and guides.
- They have a good appetite and are not picky about food.
Labradors also have their downsides :
- are genetically predisposed to a number of diseases ;
- rather gluttonous and costly in nutrition, as they consume about 1 pound of food per day;
- because of their friendliness, they will not be able to become guards;
- they like to gnaw everything, respectively, they can ruin expensive things;
- since the dog is large, a small apartment is not suitable for accommodating one.
Distinctive Features and Parameters
- Large, sturdy dog with a wide chest and powerful paws
- Wide wedge-shaped head
- Slightly tapering straight nose
- Hanging ears, curved-forward, triangular
- Almond-shaped, hazel or brown eyes
- The teeth are straight, proportional
- The tail of medium length, tapering towards the end

Health and longevity
The average lifespan of a Labrador is 10-14 years. Despite its activity, this breed suffers from a variety of genetic diseases.
Obesity comes first as these dogs love to eat everything. It also exacerbates other existing illnesses.
The most common diseases in Labradors are :
- dysplasia of the elbow and hip joints ;
- eye problems – cataracts, retinal detachment;
- osteochondrosis;
- lack of thyroid hormones;
- skin diseases;
- nose problems, cracks, and crusts.
Red Fox Lab Price range
The cost of a puppy consists of a number of indicators. First of all, you need to decide on the purpose of adoption.
If It’s just a friend for the family, without the prospect of participating in exhibitions, then you can take a puppy without a pedigree. They will be much cheaper.
For the rest, the price depends on the following parameters :
- The richer the pedigree, the higher the cost. Titled and distinguished ancestors play an important role.
- The presence or absence of vaccinations.
- The gender of the dog. Novice dog owners are afraid to take females for maintenance because of leaks. Due to this, males are more popular and have become more expensive.
- Breeder. From kennels or dog handlers, are much more expensive than ordinary breeders.
- Puppy appearance. The more the dog meets the breed standards, the more expensive its cost.
Specifically, red dogs fall under the breed standard, however, as mentioned above, experts may not approve of the color. Based on this, the cost of a red puppy will be noticeably lower than a black one. A red lox lab has an average price of 1200 to 1800$.
Why do red fox puppies cost more?
Although fox red labradors have been increasing lately, their light yellow “brothers” are still much more prevalent.
The price of a red fox labrador puppy with all the certifications and important bloodlines can range from 2,500 to 3,000 Dollars.
How to choose a red puppy?
The optimal age for buying a puppy is 2 months or 3 months.
By this time, the breeder should have done all the necessary vaccinations and socialized the dog. The color will already be permanent.
What to look for when choosing a puppy :
- proportional physique
- shiny pure wool
- smart looking eyes
- interest in a person
- nice smell
Responsible breeders will always help in the future if you have any questions about the content.
The Labrador Retriever is the perfect friend dog. Whether you are an elderly person, a young family with children, or just leading an active lifestyle, this dog will suit everyone. Pay more attention to It and It will answer you with great and sincere love and devotion.


